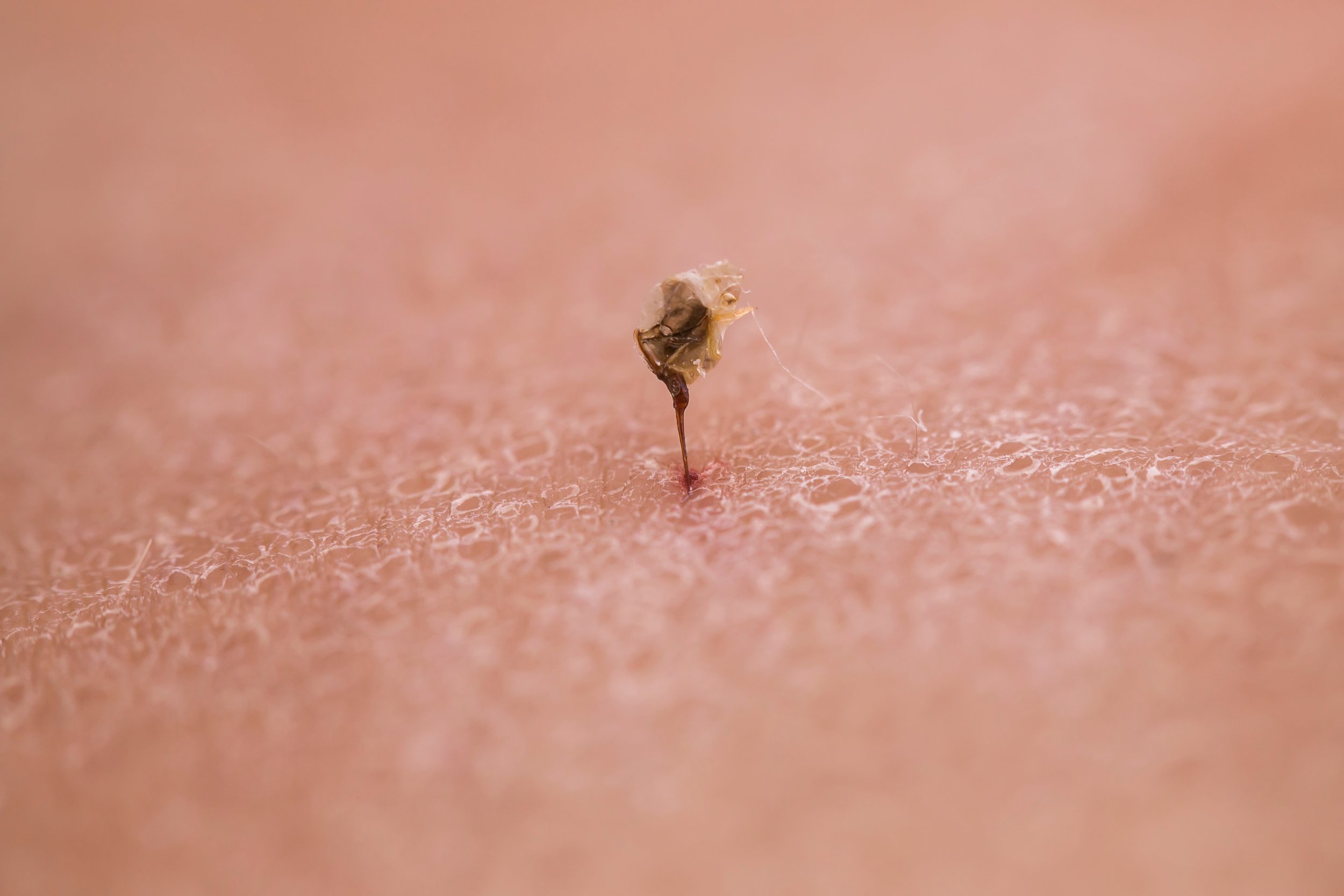
Bee Stings
Treatment for a bee sting typically involves addressing the symptoms, which can include pain, redness, itching, and swelling. Here are some steps that you can take to treat a bee sting:
Remove the stinger: If the stinger is still in the skin, remove it as soon as possible. Do not use tweezers, as this can squeeze more venom into the skin. Instead, use a flat object, such as a credit card, to scrape the stinger out.
Clean the area: Clean the sting site with soap and water to reduce the risk of infection.
Apply a cold pack: To help reduce pain and swelling, apply a cold pack or a bag of frozen vegetables to the sting site for 10-15 minutes at a time. Repeat as needed.
Take over-the-counter pain medication: To help ease pain and discomfort, you can take over-the-counter pain medication such as ibuprofen or paracetamol.
Apply a cream or lotion: To help reduce itching and redness, you can apply a cream or lotion designed to treat bites and stings.
Watch for signs of a severe allergic reaction: In rare cases, a bee sting can cause a severe allergic reaction, known as anaphylaxis. Signs of anaphylaxis include difficulty breathing, hives, swelling of the face and throat, and a rapid heartbeat. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
It's also important to note that people who are allergic to bees or have a history of severe allergic reactions should carry an adrenaline auto-injector (EpiPen or AnaPen) with them at all times and know how to use it.
It's important to be aware of the presence of bees and to avoid them, if possible, as well as educating oneself about the signs of an allergic reaction and how to act in case of one.