How to Handle a Bee Sting: First Aid Basics
Picture this: You’re enjoying a sunny day outdoors when you or someone nearby yelps in pain after a sudden sting. Would you know how to help? Bee stings are common, and while most are harmless, some can lead to severe allergic reactions requiring urgent care.
Signs and Symptoms of a Bee Sting
Bee stings can cause a range of reactions, from mild irritation to severe anaphylaxis. Here's what to look for:
Mild Reaction:
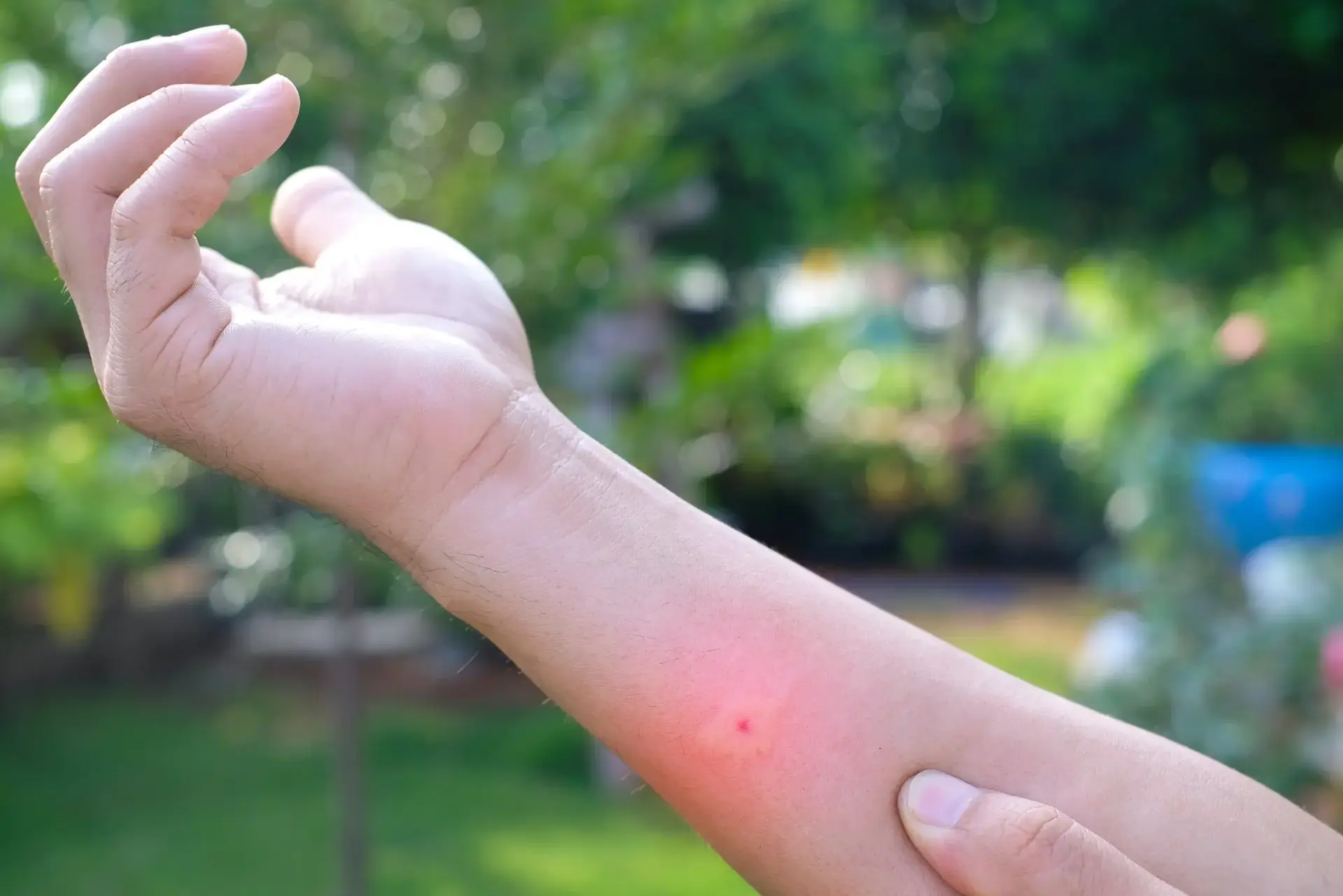
- Sharp, burning pain at the sting site.
- Redness and swelling around the area.
- A small white spot where the stinger punctured the skin.
Moderate Reaction:
- Increased swelling (up to 10 cm or more).
- Redness and warmth around the sting site.
- Symptoms may persist for a day or two.
Severe Allergic Reaction (Anaphylaxis):
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing.
- Swelling of the face, lips, or throat.
- Rapid heartbeat or dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain.
- Loss of consciousness.
Anaphylaxis is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. Call 000 if these symptoms appear.
- Remove the Stinger:
- Bees leave their stinger behind, along with a venom sac. Use a flat object, like a credit card, to scrape the stinger out gently.
- Avoid squeezing the stinger, as this can release more venom.
- Wash the Area:
- Clean the sting site with soap and water to reduce the risk of infection.
- Apply a Cold Pack:
- Use a cold pack or cloth-wrapped ice to reduce pain and swelling. Apply for 10-15 minutes at a time.
- Take Pain Relief:
- Use paracetamol or ibuprofen to manage pain if needed.
- For itching or swelling, an antihistamine like loratadine or cetirizine may help.
- Monitor for Allergic Reactions:
- Watch for any signs of anaphylaxis, particularly within the first 30 minutes after the sting.
What to Do for Severe Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
- Call 000 immediately.
- If the person has an adrenaline auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen or Anapen), administer it according to the instructions.
- Keep the person calm and lying down. Elevate their legs if they feel faint.
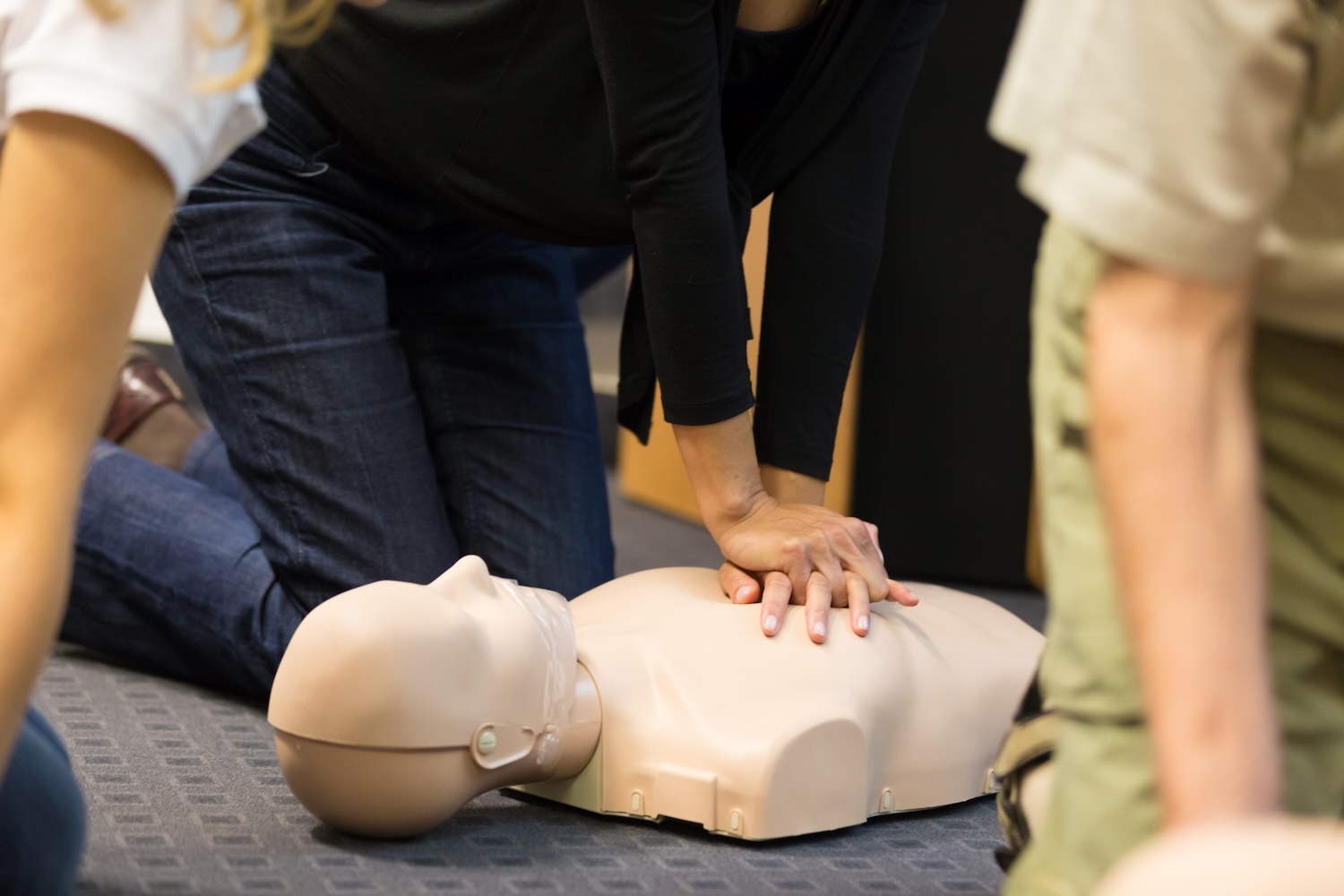
- Monitor their breathing and be prepared to start CPR if necessary.
Preventing Bee Stings
- Wear protective clothing in areas where bees are active.
- Avoid bright colours and floral scents, which attract bees.
- Keep food and sugary drinks covered outdoors.
Learn More About Managing Allergic Reactions
To learn more about managing bee stings and the associated allergic reactions, book one of our first aid courses with Australian Pacific Training Solutions.